Logging out other users from the command line
You may use who to check which users are logged in:
who
You can log-out the user by sending the KILL signal to the user-process with:
sudo pkill -KILL -u
How to ban an IP address in Fail2Ban
Identify the jail you want to apply the ban to:
sudo fail2ban-client status
Run the following command, replacing with the jail’s name (e.g., sshd) and with the IP you want to block:
sudo fail2ban-client set banip
Check if the IP is now listed under the banned IP list for that jail:
sudo fail2ban-client status
What is the difference between docker and docker-compose
docker manages single containers
docker-compose manages multiple container applications
changeme. A default credential scanner
changeme picks up where commercial scanners leave off. It focuses on detecting default and backdoor credentials and not necessarily common credentials. It’s default mode is to scan HTTP default credentials, but has support for other credentials.
changeme is designed to be simple to add new credentials without having to write any code or modules. changeme keeps credential data separate from code. All credentials are stored in yaml files so they can be both easily read by humans and processed by changeme. Credential files can be created by using the ./changeme.py --mkcred tool and answering a few questions.
deb.sury.org
The main repositories now contain both PHP 5.6, PHP 7.0-7.4 and PHP 8.0-8.3 coinstallable together.
Using Free Let’s Encrypt SSL/TLS Certificates with NGINX
sudo certbot --nginx -d example.com -d www.example.comFixing the “Kernel Panic – not syncing: VFS: Unable to mount root fs on unknown-block(0,0)” Error After Upgrading Ubuntu
Regenerate initramfs for the New Kernel
To fix the issue, you need to regenerate the initramfs for the new kernel version. Run the following command in the terminal:
sudo update-initramfs -u -k <version>
Replace <version> with the actual kernel version string for the kernel that you were unable to boot into. For example, it might look something like 4.15.0-36-generic.
You can find the kernel version by running uname -r if needed.
Update GRUB
Once the initramfs has been successfully generated, update the GRUB bootloader by running:
sudo update-grub
This command ensures that GRUB recognizes the updated kernel and its corresponding initramfs.
Who is using chroot with php-fpm? Is it worth it?
I don’t use chroot, but the default setup for modern versions of FPM already compartmentalizes everything adequately for example, the private /tmp directory. I agree with others that chroot is an outdated way of doing things.
Also, I use SELinux…yet another way of achieving many of the same goals of chrooting. I’d highly recommend setting up SELinux if you are not already using it. If you’re concerned enough about security that you’d even think of chrooting php-fmp, you probably want to set up SELinux and have it on “Enforcing” (it’s useless on “Permissive” mode, that’s really only suitable for the configuration phase of test servers.) Not only will it provide security with PHP, but you get a whole bunch of other security benefits of it.
I have done some pretty sophisticated things with a web server under SELinux, requiring me to manually change a number of policies, and while I have had a few prolonged sessions of frustration, maybe 3-4 hours at a time of banging my head against the wall trying to get the permissions set up properly, it is totally worth it. It’s all up-front work, and once you learn how to do it it’s very easy.
wordfence-cli. Wordfence malware and vulnerability scanner command line utility
Wordfence CLI is an open source, high performance, multi-process security scanner, written in Python, that quickly scans network filesystems to detect PHP/other malware and WordPress vulnerabilities. CLI is parallelizable, can be scheduled, can accept input via pipe, and can pipe output to other commands.
What is a TPM and why isn’t mine working?
A TPM, or Trusted Platform Module, is a security chip that can be embedded in a laptop or plugged into most desktop PCs. It’s basically a lockbox for keys, as well as an encryption device a PC can use to boost its security.
Nginx Configuration for Matomo
This is a small nginx configuration that should help you get your own Matomo instance running and start collecting your own analytics.
Configure CGI executable Environment on Nginx
root@www:~# apt -y install fcgiwrap
root@www:~# vi /etc/nginx/fcgiwrap.conf
# create new
# for example, enable CGI under [/cgi-bin]
location /cgi-bin/ {
gzip off;
root /var/www;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/fcgiwrap.socket;
include /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
}
root@www:~# mkdir /var/www/cgi-bin
root@www:~# chmod 755 /var/www/cgi-bin
# add settings into [server] section of a site definition
root@www:~# vi /etc/nginx/sites-available/default
server {
.....
.....
include fcgiwrap.conf;
}
root@www:~# systemctl enable fcgiwrap
root@www:~# systemctl reload ngin
How to Delete a User on Linux (and Remove Every Trace)
The command to use depends on which distribution of Linux you’re using. For Debian based Linux distributions, the command is deluser, and for the rest of the Linux world, it is userdel.
sudo deluser –remove-home USERNAME
Node Version Manager (nvm)
Node Version Manager – POSIX-compliant bash script to manage multiple active node.js versions
How to See All Devices on Your Network With nmap on Linux
nmap is a network mapping tool. It works by sending various network messages to the IP addresses in the range we’re going to provide it with it. It can deduce a lot about the device it is probing by judging and interpreting the type of responses it gets.
Let’s kick off a simple scan with nmap. We’re going to use the -sn (scan no port) option. This tells nmap to not probe the ports on the devices for now. It will do a lightweight, quick scan.
Even so, it can take a little time for nmap to run. Of course, the more devices you have on the network, the longer it will take. It does all of its probing and reconnaissance work first and then presents its findings once the first phase is complete. Don’t be surprised when nothing visible happens for a minute or so.
The IP address we’re going to use is the one we obtained using the ip command earlier, but the final number is set to zero. That is the first possible IPAddress on this network. The “/24” tells nmap to scan the entire range of this network. The parameter “192.168.4.0/24” translates as “start at IP address 192.168.4.0 and work right through all IP addresses up to and including 192.168.4.255”.
Note we are using sudo.
sudo nmap -sn 192.168.4.0/24
10+ commands to list all systemctl services with status
To list all the service unit files which are currently in enabled state use –state=enabled
# systemctl list-unit-files --type=service --state=enabled
Make all new files in a directory accessible to a group
change the directory’s ACL to give the group write permissions and to make these permissions inherited by newly created files. Under Linux:
setfacl -d -m group:GROUPNAME:rwx /path/to/directory setfacl -m group:GROUPNAME:rwx /path/to/directory
How to enable HTTP/2 support in Apache
Enable HTTP/2 module
Apache’s HTTP/2 support comes from the mod_http2 module. Enable it from:
a2enmod http2
apachectl restart
If above commands do not work in your system (which is likely the case in CentOS/RHEL), use LoadModule directive in httpd configuration directory to enable http2 module.
Add HTTP/2 Support
We highly recommend you enable HTTPS support for your web site first. Most web browser simply do not support HTTP/2 over plain text. Besides, there are no excuses to not use HTTPS anymore. HTTP/2 can be enabled site-by-site basis. Locate your web site’s Apache virtual host configuration file, and add the following right after the opening
Protocols h2 http/1.1
How to Run Bash Script as Root During Startup on Linux
…start off by writing “@reboot.” The reboot command is key here as it tells the cron on reboot this command to run every single time. Directly after reboot, add the full file path to the bash script.
@reboot /home/derrik/startupscript.sh
xdg and autostart in Linux X server regardless the desktop environment
There two main paths to look for entries to autostart:
/etc/xdg/autostart – called system-wide and most of the application will place files when they are installed.
[user’s home]/.config/autostart – user’s applications to start when the user logs in .
There is a security problem here, which is sometimes installing a package will place an autostart file there because the maintainer decided it is important but the package might be just a dependency and the next time the user logs in unwanted program might execute and open ports!
Run a WP-CLI command as a given WordPress user
Use the –user=
Xsession
System-wide configuration of the Debian X session consists mainly of options inside the /etc/X11/Xsession.options file, and scripts inside the /etc/X11/Xsession.d directory. These scripts are all dotted in by a single /bin/sh shell, in the order determined by sorting their names. Administrators may edit the scripts, though caution is advised if you are not comfortable with shell programming.
Better font rendering in linux
If we’re not running a full blown desktop environment like GNOME, KDE or XFCE, the chances of getting good font rendering in a post Xorg installation after a default linux base (think of arch or voidlinux) install is zero. This guide serves as a list of todo items to get decent font rendering with these sort of installs.
Here’s How to Find Out Which Desktop Environment You are Using
Open the terminal and copy paste this command:
echo $XDG_CURRENT_DESKTOP
…simply type screenfetch in the terminal and it should show the desktop environment version along with other system information.
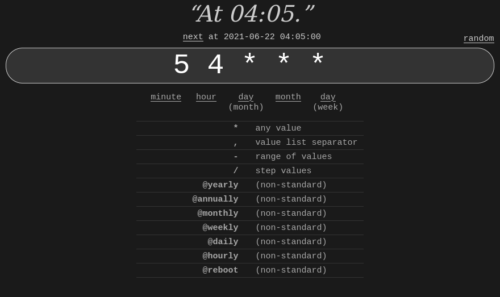
crontab guru. The quick and simple editor for cron schedule expressions
evo x weight loss buy letrozole uk 5 exercises for triceps with dumbbells
How to check for open ports on Linux
netstat -lt
Archiving a (WordPress) website with wget
I used wget, which is available on any linux-ish system (I ran it on the same Ubuntu server that hosts the sites).
wget –mirror -p –html-extension –convert-links -e robots=off -P . http://url-to-site
That command doesn’t throttle the requests, so it could cause problems if the server has high load. Here’s what that line does:
–mirror: turns on recursion etc… rather than just downloading the single file at the root of the URL, it’ll now suck down the entire site.
-p: download all prerequisites (supporting media etc…) rather than just the html
–html-extension: this adds .html after the downloaded filename, to make sure it plays nicely on whatever system you’re going to view the archive on
–convert-links: rewrite the URLs in the downloaded html files, to point to the downloaded files rather than to the live site. this makes it nice and portable, with everything living in a self-contained directory.
-e robots=off: executes the “robots off” command, telling wget to ignore any directive to ignore the site in question. This is strictly Not a Good Thing To Do, but if you own the site, this is OK. If you don’t own the site being archived, you should obey all robots.txt files or you’ll be a Very Bad Person.
-P .: set the download directory to something. I left it at the default “.” (which means “here”) but this is where you could pass in a directory path to tell wget to save the archived site. Handy, if you’re doing this on a regular basis (say, as a cron job or something…)
http://url-to-site: this is the full URL of the site to download. You’ll likely want to change this.
Web ARChive
The Web ARChive (WARC) archive format specifies a method for combining multiple digital resources into an aggregate archive file together with related information. The WARC format is a revision of the Internet Archive’s ARC_IA File Format[4] that has traditionally been used to store “web crawls” as sequences of content blocks harvested from the World Wide Web. The WARC format generalizes the older format to better support the harvesting, access, and exchange needs of archiving organizations. Besides the primary content currently recorded, the revision accommodates related secondary content, such as assigned metadata, abbreviated duplicate detection events, and later-date transformations.
Wget with WARC output
From the discussion about Working with ARCHIVE.ORG, we learn that it is important to save not just files but also HTTP headers.
To download a file and save the request and response data to a WARC file, run this:
wget “http://www.archiveteam.org/” –warc-file=”at”
This will download the file to index.html, but it will also create a file at-00000.warc.gz. This is a gzipped WARC file that contains the request and response headers (of the initial redirect and of the Wiki homepage) and the html data.
If you want to have an uncompressed WARC file, use the –no-warc-compression option:
wget “http://www.archiveteam.org/” –warc-file=”at” –no-warc-compression
Archiving Websites with Wget
When IA first started doing their thing, they came across a problem: how do you actually save all of the information related to a website as it existed at a point in time? IA wanted to capture it all, including headers, images, stylesheets, etc.
After a lot of revision the smart folks there built a specification for a file format named WARC, for Web ARCive. The details aren’t super important, but the gist is that it will preserve everything, including headers, in a verifiable, indexed, checksumed format.
Archiving a website with wget
wget –recursive –convert-links -mpck –html-extension –user-agent=”Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/88.0.4324.146 Safari/537.36.” -e robots=off site.com
DNS.WATCH. Fast, free and uncensored
We are operating the following DNS resolvers. All our resolvers can be used free of charge.
The resolvers are alive since 2014 and the project remains maintained.
84.200.69.80
resolver1.dns.watch
No Logging, DNSSEC enabled
84.200.70.40
resolver2.dns.watch
No Logging, DNSSEC enabled
Block with /etc/hosts
I run a shell script on my laptop to block ads, trackers, and malicious websites at the DNS host level. I also use 1.1.1.1 as the DNS resolver on my laptop and phone. This article describes why, alternatives, and trade-offs.
How to Find My DNS Server IP Address in Linux
$ cat /etc/resolv.conf
Block Unwanted Advertisements with a Hosts File on Linux
I surf the web an awful lot, probably slightly more than your average 13 year old geek. I notice that a lot of sites load rather slowly mostly because your waiting on content from outside the specific domain. For example if you go to a website like thechive.com (one of my favorites) you will notice it takes quite a long time loading the ads. It would be nice if you could block advertisements… oh you can?
Although I mentioned thechive.com I spend most of my time on the net looking for information, not entertainment. These ads really hinder my search speed!
So here is a quick way you can block all the ads. Not only will your surfing be faster but you will also save some bandwidth.
First off I would like to thank the fine folks at http://winhelp2002.mvps.org/ for doing all the leg work and collecting all the data necessary for this to work.
Awesome-Selfhosted
A list of Free Software network services and web applications which can be hosted on your own servers
What is the difference between venv, pyvenv, pyenv, virtualenv, virtualenvwrapper, pipenv, etc?
PyPI packages not in the standard library:
virtualenvis a very popular tool that creates isolated Python environments for Python libraries. If you’re not familiar with this tool, I highly recommend learning it, as it is a very useful tool, and I’ll be making comparisons to it for the rest of this answer.It works by installing a bunch of files in a directory (eg:
env/), and then modifying thePATHenvironment variable to prefix it with a custombindirectory (eg:env/bin/). An exact copy of thepythonorpython3binary is placed in this directory, but Python is programmed to look for libraries relative to its path first, in the environment directory. It’s not part of Python’s standard library, but is officially blessed by the PyPA (Python Packaging Authority). Once activated, you can install packages in the virtual environment usingpip.pyenvis used to isolate Python versions. For example, you may want to test your code against Python 2.7, 3.6, 3.7 and 3.8, so you’ll need a way to switch between them. Once activated, it prefixes thePATHenvironment variable with~/.pyenv/shims, where there are special files matching the Python commands (python,pip). These are not copies of the Python-shipped commands; they are special scripts that decide on the fly which version of Python to run based on thePYENV_VERSIONenvironment variable, or the.python-versionfile, or the~/.pyenv/versionfile.pyenvalso makes the process of downloading and installing multiple Python versions easier, using the commandpyenv install.pyenv-virtualenvis a plugin forpyenvby the same author aspyenv, to allow you to usepyenvandvirtualenvat the same time conveniently. However, if you’re using Python 3.3 or later,pyenv-virtualenvwill try to runpython -m venvif it is available, instead ofvirtualenv. You can usevirtualenvandpyenvtogether withoutpyenv-virtualenv, if you don’t want the convenience features.virtualenvwrapperis a set of extensions tovirtualenv(see docs). It gives you commands likemkvirtualenv,lssitepackages, and especiallyworkonfor switching between differentvirtualenvdirectories. This tool is especially useful if you want multiplevirtualenvdirectories.pyenv-virtualenvwrapperis a plugin forpyenvby the same author aspyenv, to conveniently integratevirtualenvwrapperintopyenv.pipenvaims to combinePipfile,pipandvirtualenvinto one command on the command-line. Thevirtualenvdirectory typically gets placed in~/.local/share/virtualenvs/XXX, withXXXbeing a hash of the path of the project directory. This is different fromvirtualenv, where the directory is typically in the current working directory.pipenvis meant to be used when developing Python applications (as opposed to libraries). There are alternatives topipenv, such aspoetry, which I won’t list here since this question is only about the packages that are similarly named.
Standard library:
pyvenvis a script shipped with Python 3 but deprecated in Python 3.6 as it had problems (not to mention the confusing name). In Python 3.6+, the exact equivalent ispython3 -m venv.venvis a package shipped with Python 3, which you can run usingpython3 -m venv(although for some reason some distros separate it out into a separate distro package, such aspython3-venvon Ubuntu/Debian). It serves the same purpose asvirtualenv, but only has a subset of its features (see a comparison here).virtualenvcontinues to be more popular thanvenv, especially since the former supports both Python 2 and 3.
Recommendation for beginners:
This is my personal recommendation for beginners: start by learning virtualenv and pip, tools which work with both Python 2 and 3 and in a variety of situations, and pick up other tools once you start needing them.
git – getting ALL previous version of a specific file/folder
The script would:
– extract all file versions to /tmp/all_versions_exported
– take 1 argument – relative path to the file inside git repo
– give result filenames numeric prefix (sortable)
– mention inspected filename in result files (to tell apples apart from oranges:)
– mention commit date in the result filename (see output example below)
– not create empty result files
Synchronize Files With rsync
Automatic Syncing With SSH Keys
#!/usr/bin/env bash
rsync -az –delete /home/kevin/source/ server.example.com:/home/kevin/destination
Rsync (Remote Sync): 10 Practical Examples of Rsync Command in Linux
Copy/Sync a File on a Local Computer
[root@tecmint]# rsync -zvh backup.tar /tmp/backups/
Copy/Sync a Directory on Local Computer
[root@tecmint]# rsync -avzh /root/rpmpkgs /tmp/backups/
How to clear the APT cache
Clear the APT cache to reclaim disk space used by the downloaded packages.